|
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
聚合物塗料(包括環氧樹脂,聚氨酯和丙烯酸酯)通常用於保護金屬偽影免受長期暴露於光,熱,氧氣和濕度。它們是輕巧,透明,水密的,可以強烈粘附在其保存的材料上。

A new study has cast into doubt a common technique used in the integration of old metal artifacts.
一項新的研究使人們懷疑一種用於整合舊金屬偽像整合的通用技術。
The "momentous and concerning" findings, which are published in American Chemical Society (ACS) Focal Point, indicate that some transparent resin coatings react with iron-containing metals and can cause damage.
在美國化學學會(ACS)焦點上發表的“重要和有關”的發現表明,某些透明的樹脂塗層與含鐵金屬反應,並可能造成損害。
A crew from China's Beijing University of Chemical Technology created a non-invasive fluorescence imaging technique that reveals the early signs of the harmful chemical reactions. It could be used to decide on the integration state and possible dangers for other artifact preservation, decreasing the harm to the valuable artifacts.
中國北京化學技術大學的一名工作人員創建了一種非侵入性熒光成像技術,揭示了有害化學反應的早期跡象。它可以用來確定整合狀態和對其他人工製品保存的可能危險,從而減少對有價值的人工製品的傷害。
Polymeric coatings, together with epoxy, polyurethane, and acrylics, are commonly used to shield metal artifacts from long-term exposure to mild, heat, oxygen, and humidity. They are lightweight, transparent, watertight, and can adhere powerfully to the materials they preserve.
聚合物塗層以及環氧樹脂,聚氨酯和丙烯酸酯通常用於屏蔽金屬偽像免受長期暴露於輕度,熱,氧氣和濕度。它們是輕巧,透明,水密的,可以強大地粘附在其保存的材料上。
However, there has been restricted analysis of what occurs to the coatings as they age and how this impacts the metal artifacts. This is because it is challenging to monitor what is happening at the boundary where the materials make contact.
但是,對塗料隨著年齡的增長以及這如何影響金屬偽像的塗料發生了限制分析。這是因為監視材料接觸的邊界處發生的事情是具有挑戰性的。
The new 3-dimensional fluorescence imaging technique, which is described in ACS Focal Point, indicates early signs of corrosion on iron-containing metal.
新的3維熒光成像技術在ACS焦點中進行了描述,表明了含鐵金屬腐蝕的早期跡象。
The researchers coated forged iron with the acrylic resin B72—the most widely used polymer in metal artifacts—and sped up its ageing method by applying UV and warmth for 30 hours. They observed no fluorescence on freshly coated forged iron, but the fluorescence depth at the resin-metal interface increased steadily after 3 hours.
研究人員用丙烯酸樹脂B72(金屬偽像中使用最廣泛的聚合物)塗了鍛鐵,並通過塗抹紫外線和溫暖30小時來加速其老化方法。他們觀察到新鮮塗層的鍛鐵沒有熒光,但是三個小時後,樹脂金屬界面的熒光深度穩定增加。
"It is surprising to acknowledge that the aged polymers can generate hazardous carboxyl teams and responsive hydroxyl radicals, inducing the oxidation and corrosion of the metal artifacts," the researchers write.
研究人員寫道:“令人驚訝的是,老化的聚合物可以產生危險的羧基和響應式羥基自由基,從而誘導金屬偽像的氧化和腐蝕。”
"In turn, the generated metallic ions could further worsen the ageing of polymer coatings."
“反過來,產生的金屬離子可能會進一步惡化聚合物塗層的衰老。”
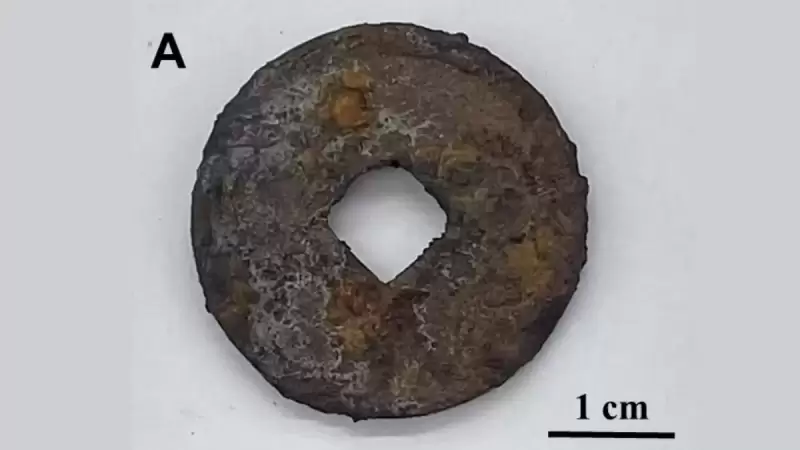
They carried out the same experiment on a rusty iron coin about 1000 years old, from the Chinese Northern Tune Dynasty, and found that the aged polymer coating made the artifact rustier.
他們從中國北部的曲子王朝進行了大約1000年的生鏽鐵幣進行同樣的實驗,發現老化的聚合物塗層使工件變得生鏽了。
"These findings raised a timely alarm for the integration potential and possible menace of polymer coatings on metal artifacts," the authors write.
作者寫道:“這些發現引起了及時的警報,以使聚合物塗料在金屬偽像的範圍內的整合潛力和可能的威脅。”
They advise that more analysis must be done to decide on how coatings can be optimised for artifact integration.
他們建議必須進行更多分析以決定如何優化塗料以進行工件整合。
"We should strengthen the analysis on the modification of polymer coatings, together including the structural design and preparation optimisation, to exclude the existence of defects or pores in the polymers," they write.
他們寫道:“我們應該加強對聚合物塗層的修飾的分析,包括結構設計和製備優化,以排除聚合物中缺陷或孔的存在。”
"Employment of a particular stabiliser, or anti-ageing additives, into polymer coatings is also needed. These actions would advertise the protective potential of polymer coatings and decrease the secondary harm to cultural artifacts."output: When precious relics are unearthed by archaeologists, it’s the job of conservators to ensure they’re passed on to future generations by protecting them from further degradation.
“還需要將特定穩定劑或抗衰老添加劑塗抹到聚合物塗料中。這些動作將宣傳聚合物塗料的保護潛力,並減少對文化偽像的次要危害。”輸出:當寶貴的遺物被考古學家發掘出來時,這是由考古學家發掘的,這是確保將來通過保護他們的保護者的工作,以確保他們能夠將其進一步保護。
But a new study has cast into doubt a common technique used in the conservation of ancient metal artefacts.
但是,一項新的研究使人們懷疑一種用於保護古代金屬人工製品的通用技術。
The “significant and alarming” findings, which are published in American Chemical Society (ACS) Central Science, indicate that some clear resin coatings react with iron-containing metals and can cause damage.
在美國化學學會(ACS)中央科學上發表的“重要而令人震驚的”發現表明,一些透明的樹脂塗層與含鐵金屬的反應,並可能造成損害。
A team from China’s Beijing University of Chemical Technology developed a non-invasive fluorescence imaging strategy that reveals the early signs of the damaging chemical reactions.
中國北京化學技術大學的一個團隊開發了一種非侵入性熒光成像策略,揭示了破壞性化學反應的早期跡象。
They say it could be used to determine the “conservation state and potential risks for other artifact preservation, minimising the damage to the valuable artifacts.”
他們說,它可以用來確定“保護狀態和其他人工製品保存的潛在風險,從而最大程度地減少對寶貴人工製品的損害。”
Polymer coatings – including epoxy, polyurethane, and acrylics – are commonly used to protect metal artifacts from long-term exposure to light, heat, oxygen and humidity. They are lightweight, transparent, watertight, and can adhere strongly to the materials they preserve.
聚合物塗料(包括環氧樹脂,聚氨酯和丙烯酸酯)通常用於保護金屬偽影免受長期暴露於光,熱,氧氣和濕度。它們是輕巧,透明,水密的,可以強烈粘附在其保存的材料上。
However, there has been limited research on what happens to polymer coatings as they age and how this affects iron-containing metals. This is because it is difficult to monitor what is happening at the boundary where the materials contact each other.
但是,關於聚合物塗料隨著年齡的增長以及這如何影響含鐵金屬的研究有限。這是因為很難監視材料相互接觸的邊界處發生的事情。
The new 3-dimensional fluorescence imaging technique, which is described in ACS Central Science, indicates early signs of corrosion and rust on iron-containing metal.
在ACS中央科學中描述的新型3維熒光成像技術表明,含鐵金屬的腐蝕和生鏽的早期跡象。
The researchers coated cast iron with the acrylic resin B72 – the most widely used polymer in metal artifacts – and sped up its ageing process by applying UV and warmth for 30 hours. They observed no fluorescence on freshly coated cast iron, but the fluorescence intensity at the resin-metal interface increased steadily after 3 hours.
研究人員將鑄鐵與丙烯酸樹脂B72(金屬偽像中最廣泛使用的聚合物)塗覆,並通過塗抹紫外線和溫暖30小時來加速其衰老過程。他們觀察到新鮮塗層的鑄鐵沒有熒光,但是3小時後樹脂金屬界面的熒光強度穩定增加。
“It is surprising to acknowledge that the aged polymers can generate hazardous carboxyl groups and reactive hydroxyl radicals, inducing the oxidation and corrosion of the metal artifacts,” ,” the researchers write.
研究人員寫道:“令人驚訝的是,老化的聚合物可以產生有害的羧基和反應性羥基自由基,從而誘導金屬偽像的氧化和腐蝕。”
“In turn, the generated metallic ions could further aggravate the aging of polymer coatings.”
“反過來,產生的金屬離子可以進一步加劇聚合物塗層的衰老。”
They carried out the same experiment on a rusty iron coin about 1000 years old, from the Chinese Northern Song Dynasty, and found that the aged polymer coating made the artifact rustier.
他們從中國北部歌曲王朝的一枚生鏽的鐵硬幣進行了同樣的實驗,發現老化的聚合物塗層使工件變得生鏽了。
“These findings raised a timely alarm for the conservation ability and potential threat of polymer coatings on metal artifacts,” the authors write.
作者寫道:“這些發現引發了及時的警報,以徵求金屬偽像的聚合物塗料的潛在威脅。”
They suggest more research must be done to determine
他們建議必須進行更多研究以確定
免責聲明:info@kdj.com
所提供的資訊並非交易建議。 kDJ.com對任何基於本文提供的資訊進行的投資不承擔任何責任。加密貨幣波動性較大,建議您充分研究後謹慎投資!
如果您認為本網站使用的內容侵犯了您的版權,請立即聯絡我們(info@kdj.com),我們將及時刪除。
-

- 比特幣(BTC)價格動作:公牛眼睛$ 100K,但必須捍衛關鍵水平
- 2025-04-27 06:55:12
- 比特幣現在的交易高於94,000美元的水平,在最近的低點急劇恢復後,比特幣表現出強勁的勢頭。
-

-

-

-

-

- 580萬美元的利用後,LoopsCale暫停了貸款市場
- 2025-04-27 06:45:12
- 分散的金融(DEFI)平台LoopsCale在剝削後暫時暫停了其貸款業務,導致損失約580萬美元。
-

- 隨著Altcoins的發展,虛擬貨幣市場的令人印象深刻的恢復持續
- 2025-04-27 06:40:12
- 虛擬貨幣市場繼續表現出令人印象深刻的恢復,在比特幣最近復興的驅動下,替代加密貨幣越來越基礎。
-

-