|
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
エポキシ、ポリウレタン、アクリルを含むポリマーコーティングは、一般に、光、熱、酸素、湿度への長期的な曝露から金属製のアーティファクトを保護するために使用されます。それらは軽量で、透明で、水密であり、保存する材料に強く固執することができます。

A new study has cast into doubt a common technique used in the integration of old metal artifacts.
新しい研究は、古い金属製のアーティファクトの統合に使用される一般的な手法を疑うことを疑います。
The "momentous and concerning" findings, which are published in American Chemical Society (ACS) Focal Point, indicate that some transparent resin coatings react with iron-containing metals and can cause damage.
American Chemical Society(ACS)の焦点に掲載されている「重要かつ懸念される」調査結果は、一部の透明な樹脂コーティングが鉄含有金属と反応し、損傷を引き起こす可能性があることを示しています。
A crew from China's Beijing University of Chemical Technology created a non-invasive fluorescence imaging technique that reveals the early signs of the harmful chemical reactions. It could be used to decide on the integration state and possible dangers for other artifact preservation, decreasing the harm to the valuable artifacts.
中国の北京化学技術大学の乗組員は、有害な化学反応の初期兆候を明らかにする非侵襲的な蛍光イメージング技術を作成しました。統合状態と他のアーティファクト保存の可能性のある危険を決定し、貴重なアーティファクトへの害を減らすために使用できます。
Polymeric coatings, together with epoxy, polyurethane, and acrylics, are commonly used to shield metal artifacts from long-term exposure to mild, heat, oxygen, and humidity. They are lightweight, transparent, watertight, and can adhere powerfully to the materials they preserve.
ポリマーコーティングは、エポキシ、ポリウレタン、およびアクリルとともに、一般的に、軽度、熱、酸素、湿度への長期暴露から金属製のアーティファクトを保護するために使用されます。それらは軽量で、透明で、水密であり、保存する材料に強力に付着することができます。
However, there has been restricted analysis of what occurs to the coatings as they age and how this impacts the metal artifacts. This is because it is challenging to monitor what is happening at the boundary where the materials make contact.
ただし、コーティングが加齢とともに発生するものと、これが金属製のアーティファクトにどのように影響するかについての分析が制限されています。これは、材料が接触する境界で何が起こっているのかを監視するのが難しいためです。
The new 3-dimensional fluorescence imaging technique, which is described in ACS Focal Point, indicates early signs of corrosion on iron-containing metal.
ACS焦点で説明されている新しい3次元蛍光イメージング技術は、鉄含有金属の腐食の初期兆候を示しています。
The researchers coated forged iron with the acrylic resin B72—the most widely used polymer in metal artifacts—and sped up its ageing method by applying UV and warmth for 30 hours. They observed no fluorescence on freshly coated forged iron, but the fluorescence depth at the resin-metal interface increased steadily after 3 hours.
研究者は、金属製アーティファクトで最も広く使用されているポリマーであるアクリル樹脂B72で鍛造鉄をコーティングし、UVと暖かさを30時間適用することにより、その老化方法を増やしました。彼らは、新たにコーティングされた鍛造鉄に蛍光を観察しなかったが、樹脂金属界面の蛍光深さは3時間後に着実に増加した。
"It is surprising to acknowledge that the aged polymers can generate hazardous carboxyl teams and responsive hydroxyl radicals, inducing the oxidation and corrosion of the metal artifacts," the researchers write.
「老化したポリマーが危険なカルボキシルチームと反応性のあるヒドロキシルラジカルを生成し、金属製アーティファクトの酸化と腐食を誘発することができることを認めることは驚くべきことです」と研究者は書いています。
"In turn, the generated metallic ions could further worsen the ageing of polymer coatings."
「次に、生成された金属イオンは、ポリマーコーティングの老化をさらに悪化させる可能性があります。」
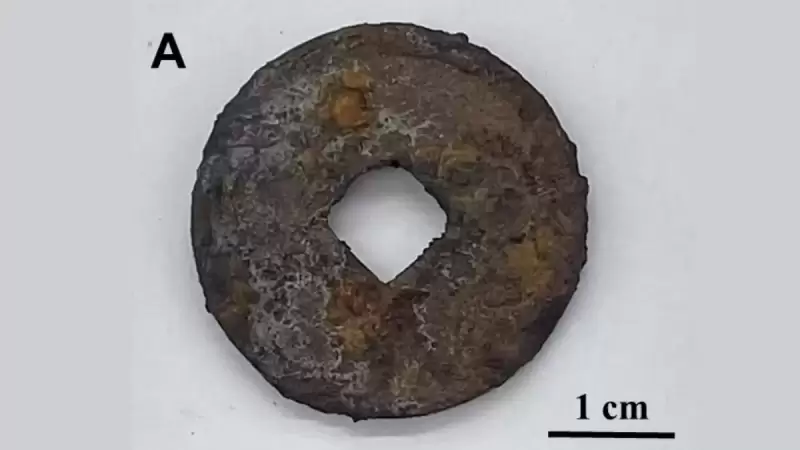
They carried out the same experiment on a rusty iron coin about 1000 years old, from the Chinese Northern Tune Dynasty, and found that the aged polymer coating made the artifact rustier.
彼らは、中国北部のチューン王朝から約1000年前のさびた鉄のコインで同じ実験を実施し、老化したポリマーコーティングがアーティファクトを素朴にすることを発見しました。
"These findings raised a timely alarm for the integration potential and possible menace of polymer coatings on metal artifacts," the authors write.
「これらの発見は、金属製アーティファクト上のポリマーコーティングの統合の可能性と脅威の可能性のためにタイムリーなアラームを提起しました」と著者は書いています。
They advise that more analysis must be done to decide on how coatings can be optimised for artifact integration.
彼らは、コーティングをアーティファクトの統合に最適化する方法を決定するために、より多くの分析を行う必要があることをアドバイスします。
"We should strengthen the analysis on the modification of polymer coatings, together including the structural design and preparation optimisation, to exclude the existence of defects or pores in the polymers," they write.
「ポリマー内の欠陥または毛穴の存在を除外するために、構造設計と準備の最適化を含む、一緒にポリマーコーティングの修飾に関する分析を強化する必要があります」と彼らは書いています。
"Employment of a particular stabiliser, or anti-ageing additives, into polymer coatings is also needed. These actions would advertise the protective potential of polymer coatings and decrease the secondary harm to cultural artifacts."output: When precious relics are unearthed by archaeologists, it’s the job of conservators to ensure they’re passed on to future generations by protecting them from further degradation.
「特定のスタビライザーの雇用、またはポリマーコーティングへのアンチエイジング添加物も必要です。これらの作用は、ポリマーコーティングの保護の可能性を宣伝し、文化的アーティファクトへの二次的な害を減らします。
But a new study has cast into doubt a common technique used in the conservation of ancient metal artefacts.
しかし、新しい研究では、古代の金属工芸品の保全に使用される一般的な手法を疑うことが疑われています。
The “significant and alarming” findings, which are published in American Chemical Society (ACS) Central Science, indicate that some clear resin coatings react with iron-containing metals and can cause damage.
American Chemical Society(ACS)中央科学に掲載されている「重要かつ驚くべき」発見は、鉄を含む金属と反応し、損傷を引き起こす可能性があることを示しています。
A team from China’s Beijing University of Chemical Technology developed a non-invasive fluorescence imaging strategy that reveals the early signs of the damaging chemical reactions.
中国の北京化学技術大学のチームは、損傷する化学反応の初期兆候を明らかにする非侵襲的蛍光イメージング戦略を開発しました。
They say it could be used to determine the “conservation state and potential risks for other artifact preservation, minimising the damage to the valuable artifacts.”
彼らは、「他のアーティファクト保存の保全状態と潜在的なリスクを決定し、貴重なアーティファクトへの損害を最小限に抑える」ために使用できると彼らは言います。
Polymer coatings – including epoxy, polyurethane, and acrylics – are commonly used to protect metal artifacts from long-term exposure to light, heat, oxygen and humidity. They are lightweight, transparent, watertight, and can adhere strongly to the materials they preserve.
エポキシ、ポリウレタン、アクリルを含むポリマーコーティングは、一般に、光、熱、酸素、湿度への長期的な曝露から金属製のアーティファクトを保護するために使用されます。それらは軽量で、透明で、水密であり、保存する材料に強く固執することができます。
However, there has been limited research on what happens to polymer coatings as they age and how this affects iron-containing metals. This is because it is difficult to monitor what is happening at the boundary where the materials contact each other.
しかし、ポリマーコーティングが加齢とともに何が起こるか、これが鉄含有金属にどのように影響するかについての研究は限られています。これは、材料が互いに接触する境界で何が起こっているかを監視することが困難であるためです。
The new 3-dimensional fluorescence imaging technique, which is described in ACS Central Science, indicates early signs of corrosion and rust on iron-containing metal.
ACS中央科学に記載されている新しい3次元蛍光イメージング技術は、鉄含有金属の腐食と錆の初期兆候を示しています。
The researchers coated cast iron with the acrylic resin B72 – the most widely used polymer in metal artifacts – and sped up its ageing process by applying UV and warmth for 30 hours. They observed no fluorescence on freshly coated cast iron, but the fluorescence intensity at the resin-metal interface increased steadily after 3 hours.
研究者たちは、金属アーティファクトで最も広く使用されているポリマーであるアクリル樹脂B72で鋳鉄をコーティングし、UVと暖かさを30時間適用することにより、老化プロセスを増やしました。彼らは、新たにコーティングされた鋳鉄に蛍光は観察されませんでしたが、樹脂金属界面の蛍光強度は3時間後に着実に増加しました。
“It is surprising to acknowledge that the aged polymers can generate hazardous carboxyl groups and reactive hydroxyl radicals, inducing the oxidation and corrosion of the metal artifacts,” ,” the researchers write.
「老化したポリマーが危険なカルボキシル基と反応性のヒドロキシルラジカルを生成し、金属のアーティファクトの酸化と腐食を誘発することができることを認めるのは驚くべきことです」と研究者は書いています。
“In turn, the generated metallic ions could further aggravate the aging of polymer coatings.”
「次に、生成された金属イオンは、ポリマーコーティングの老化をさらに悪化させる可能性があります。」
They carried out the same experiment on a rusty iron coin about 1000 years old, from the Chinese Northern Song Dynasty, and found that the aged polymer coating made the artifact rustier.
彼らは、中国北部の歌王朝から約1000年前の錆びた鉄のコインで同じ実験を実施し、老化したポリマーコーティングがアーティファクトを騒々しくしたことを発見しました。
“These findings raised a timely alarm for the conservation ability and potential threat of polymer coatings on metal artifacts,” the authors write.
「これらの発見は、金属製のアーティファクトに対するポリマーコーティングの保存能力と潜在的な脅威に対するタイムリーなアラームを提起しました」と著者は書いています。
They suggest more research must be done to determine
彼らは、決定するためにさらに研究を行う必要があることを示唆しています
免責事項:info@kdj.com
提供される情報は取引に関するアドバイスではありません。 kdj.com は、この記事で提供される情報に基づいて行われた投資に対して一切の責任を負いません。暗号通貨は変動性が高いため、十分な調査を行った上で慎重に投資することを強くお勧めします。
このウェブサイトで使用されているコンテンツが著作権を侵害していると思われる場合は、直ちに当社 (info@kdj.com) までご連絡ください。速やかに削除させていただきます。