-
 Bitcoin
Bitcoin $120100
1.16% -
 Ethereum
Ethereum $4329
2.25% -
 XRP
XRP $3.192
-0.22% -
 Tether USDt
Tether USDt $1.000
-0.01% -
 BNB
BNB $805.2
0.47% -
 Solana
Solana $178.7
-1.85% -
 USDC
USDC $0.9998
0.00% -
 Dogecoin
Dogecoin $0.2305
-1.62% -
 TRON
TRON $0.3445
1.17% -
 Cardano
Cardano $0.7940
-1.28% -
 Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid $44.44
-1.20% -
 Chainlink
Chainlink $21.86
-2.42% -
 Stellar
Stellar $0.4423
-0.15% -
 Sui
Sui $3.728
-3.84% -
 Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash $584.8
2.19% -
 Hedera
Hedera $0.2524
-2.87% -
 Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe $1.001
-0.02% -
 Avalanche
Avalanche $23.66
-0.78% -
 Litecoin
Litecoin $124.5
0.39% -
 Toncoin
Toncoin $3.399
1.77% -
 UNUS SED LEO
UNUS SED LEO $9.002
-0.44% -
 Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu $0.00001327
-2.10% -
 Uniswap
Uniswap $11.42
2.58% -
 Polkadot
Polkadot $3.957
-2.50% -
 Cronos
Cronos $0.1696
4.50% -
 Dai
Dai $1.000
0.00% -
 Ethena
Ethena $0.8139
3.04% -
 Bitget Token
Bitget Token $4.442
-0.38% -
 Monero
Monero $271.2
2.93% -
 Pepe
Pepe $0.00001168
-2.91%
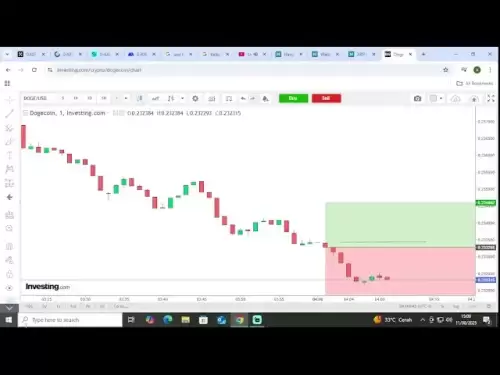
Under what circumstances is the market price order more applicable?
Market price orders are advantageous for immediate execution in volatile markets, executing large orders, liquidating positions urgently, margin trading, and running trading bots.
Feb 21, 2025 at 07:31 pm

Key Points:
- Understanding Market Price Orders vs. Limit Orders
- Circumstances Favoring Market Price Orders
- Advantages of Using Market Price Orders
- Disadvantages of Using Market Price Orders
- Best Practices for Using Market Price Orders
- FAQs
Under what circumstances is the market price order more applicable?
Market price orders are buy or sell orders that are executed immediately at the current market price. They differ from limit orders, which specify a maximum or minimum price at which the order is executed. Market price orders are typically used in volatile markets or when traders seek immediate execution.
Circumstances Favoring Market Price Orders:
- Fast-changing markets: In highly volatile markets where prices fluctuate rapidly, market price orders allow traders to enter or exit positions quickly. Limit orders may not execute in time due to price movements.
- Large order execution: Traders with large orders may prefer market price orders to avoid moving the market against them. By executing the order immediately, they minimize the impact on the price.
- Immediate liquidation: Market price orders are ideal for situations where traders need to liquidate their positions urgently, regardless of the price. This can help reduce losses or capitalize on sudden price movements.
- Margin trading: Traders using leverage may prefer market price orders to take advantage of price fluctuations. However, this strategy requires careful risk management.
- Trading bots: Automated trading systems often use market price orders for rapid trade execution based on predefined algorithms.
Advantages of Using Market Price Orders:
- Immediate execution: Market price orders guarantee immediate order execution.
- Faster in volatile markets: They are particularly effective in volatile markets where swift execution is crucial.
- Reduced slippage: In highly liquid markets, market price orders experience minimal slippage, ensuring the executed price is close to the prevailing market price.
- Simplicity: Market price orders are relatively straightforward to place, requiring only the quantity to be bought or sold.
Disadvantages of Using Market Price Orders:
- Price uncertainty: Market price orders execute at the prevailing market price, which may not be the best available.
- Slippage risk: In less liquid markets, market price orders may experience slippage, where the executed price deviates significantly from the intended price.
- Loss potential: In volatile or fast-moving markets, market price orders can result in significant losses if the market moves adversely after execution.
- Market manipulation: Market price orders can contribute to market manipulation by large traders who leverage their order size to influence price movements.
Best Practices for Using Market Price Orders:
- Use caution in volatile markets: Be aware of price volatility and limit the use of market price orders accordingly.
- Set a specific price target: Enter a specific price target for market price orders to avoid execution at undesirable prices.
- Monitor the market: Continuously monitor market conditions to assess the potential impact of market price orders.
- Consider slippage: Factor in the possibility of slippage when using market price orders.
- Manage risk: Implement proper risk management strategies, such as stop-loss orders, to mitigate potential losses.
FAQs:
Q: What is the difference between a market price order and a limit order?
A: A market price order is executed immediately at the current market price, while a limit order specifies a specific price at which the order will be executed.
Q: When should I use a market price order?
A: Market price orders are best used in fast-changing markets, for executing large orders, urgent liquidations, and leveraging extreme price fluctuations.
Q: What are the risks of using a market price order?
A: The risks include price uncertainty, slippage, loss potential, and market manipulation.
Q: How can I mitigate the risks of a market price order?
A: Set a price target, monitor the market, consider slippage, and implement proper risk management strategies.
Disclaimer:info@kdj.com
The information provided is not trading advice. kdj.com does not assume any responsibility for any investments made based on the information provided in this article. Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile and it is highly recommended that you invest with caution after thorough research!
If you believe that the content used on this website infringes your copyright, please contact us immediately (info@kdj.com) and we will delete it promptly.
- Bitcoin, Solana, MAGACOIN FINANCE: Navigating the 2025 Crypto Landscape
- 2025-08-12 00:30:13
- Cardano, ADA Holders, and Layer Brett: A Meme Coin with Real Utility?
- 2025-08-12 00:50:12
- Bitcoin, Michael Saylor, and Savvy Investors: A New Era of Digital Assets
- 2025-08-12 00:30:13
- Crypto Presales in 2025: Spotting the Next Big Thing with Analyst Insights
- 2025-08-12 00:50:12
- Cloud Mining in 2025: Bitcoin, Litecoin, and the Quest for Passive Income
- 2025-08-12 00:55:32
- Token Security, Agentic AI, Cybersecurity Guide: Navigating the New Frontier
- 2025-08-11 23:00:12
Related knowledge

Is it possible to adjust the leverage on an open position on KuCoin?
Aug 09,2025 at 08:21pm
Understanding Leverage in KuCoin Futures TradingLeverage in KuCoin Futures allows traders to amplify their exposure to price movements by borrowing fu...

What cryptocurrencies are supported as collateral on KuCoin Futures?
Aug 11,2025 at 04:21am
Overview of KuCoin Futures and Collateral MechanismKuCoin Futures is a derivatives trading platform that allows users to trade perpetual and delivery ...

What is the difference between realized and unrealized PNL on KuCoin?
Aug 09,2025 at 01:49am
Understanding Realized and Unrealized PNL on KuCoinWhen trading on KuCoin, especially in futures and perpetual contracts, understanding the distinctio...

How does KuCoin Futures compare against Binance Futures in terms of features?
Aug 09,2025 at 03:22am
Trading Interface and User ExperienceThe trading interface is a critical component when comparing KuCoin Futures and Binance Futures, as it directly i...

How do funding fees on KuCoin Futures affect my overall profit?
Aug 09,2025 at 08:22am
Understanding Funding Fees on KuCoin FuturesFunding fees on KuCoin Futures are periodic payments exchanged between long and short position holders to ...

What is the distinction between mark price and last price on KuCoin?
Aug 08,2025 at 01:58pm
Understanding the Basics of Price in Cryptocurrency TradingIn cryptocurrency exchanges like KuCoin, two key price indicators frequently appear on trad...

Is it possible to adjust the leverage on an open position on KuCoin?
Aug 09,2025 at 08:21pm
Understanding Leverage in KuCoin Futures TradingLeverage in KuCoin Futures allows traders to amplify their exposure to price movements by borrowing fu...

What cryptocurrencies are supported as collateral on KuCoin Futures?
Aug 11,2025 at 04:21am
Overview of KuCoin Futures and Collateral MechanismKuCoin Futures is a derivatives trading platform that allows users to trade perpetual and delivery ...

What is the difference between realized and unrealized PNL on KuCoin?
Aug 09,2025 at 01:49am
Understanding Realized and Unrealized PNL on KuCoinWhen trading on KuCoin, especially in futures and perpetual contracts, understanding the distinctio...

How does KuCoin Futures compare against Binance Futures in terms of features?
Aug 09,2025 at 03:22am
Trading Interface and User ExperienceThe trading interface is a critical component when comparing KuCoin Futures and Binance Futures, as it directly i...

How do funding fees on KuCoin Futures affect my overall profit?
Aug 09,2025 at 08:22am
Understanding Funding Fees on KuCoin FuturesFunding fees on KuCoin Futures are periodic payments exchanged between long and short position holders to ...

What is the distinction between mark price and last price on KuCoin?
Aug 08,2025 at 01:58pm
Understanding the Basics of Price in Cryptocurrency TradingIn cryptocurrency exchanges like KuCoin, two key price indicators frequently appear on trad...
See all articles