|
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
加密货币新闻
INDUSTRIAL waste is turning into rock in decades, much faster than the millions of years it is thought to take for it to form naturally
2025/04/28 19:07
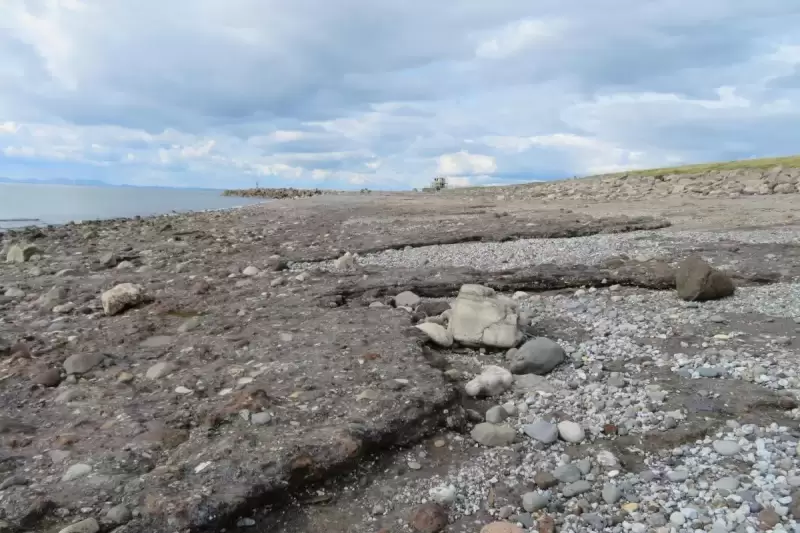

INDUSTRIAL waste is turning into rock in decades, much faster than the millions of years it is thought to take for it to form naturally, scientists have said.
An aluminium drinks can tab made since 1989 and a 1934 coin are among the items that have helped researchers understand how quickly the process is happening.
The scientists have documented a new “rapid anthropoclastic rock cycle”, which mimics natural rock cycles but involves human material over accelerated timescales.
They warn that the rapid and unplanned-for development of rock around industrial waste sites could have negative impacts on biodiversity and ecosystems, as well as land planning and coastal management.
Their findings came from analysis of a two-kilometre stretch of slag deposit, at Derwent Howe in West Cumbria, which was home to iron and steel-making foundries during the 19th and 20th centuries.
The slag deposits have formed cliffs of waste material which are being eroded by coastal waves and tides, and the team carried out detailed analysis after noticing intriguing irregular formations in the cliffs.
Dr Amanda Owen of the University of Glasgow’s School of Geographical and Earth Sciences and one of the study’s authors, said: “For a couple of hundred years, we’ve understood the rock cycle as a natural process that takes thousands to millions of years.
“What’s remarkable here is that we’ve found these human-made materials being incorporated into natural systems and become lithified – essentially turning into rock – over the course of decades instead.
“It challenges our understanding of how a rock is formed, and suggests that the waste material we’ve produced in creating the modern world is going to have an irreversible impact on our future.”
Laboratory tests helped the researchers determine that Derwent Howe’s slag materials contain deposits of calcium, iron, magnesium, and manganese.
These elements are highly chemically reactive, which is key to causing the accelerated process of rock formation.
When the slag is eroded by the sea, it exposes the material to seawater and air, which interacts with the slag’s reactive elements to create natural cements including calcite, goethite, and brucite.
These cements are the same materials that bind together natural sedimentary rocks, but the chemical reactions cause the process to happen much faster than has been assumed to happen with similar material in a natural rock cycle.
Researchers also found modern materials trapped in some of the samples, which helped them to determine how quickly the process is happening.
Dr John MacDonald, a co-author of the study, said: “We were able to date this process with remarkable precision.
“We found both a King George V coin from 1934 and an aluminium can tab with a design that we realised couldn’t have been manufactured before 1989 embedded in the material.
“This gives us a maximum timeframe of 35 years for this rock formation, well within the course of a single human lifetime.
“This is an example in microcosm of how all the activity we’re undertaking at the Earth’s surface will eventually end up in the geological record as rock, but this process is happening with remarkable, unprecedented speed.”
Researchers have warned that the process could have an impact on ecosystems and said more research is needed.
Dr David Brown, the paper’s third co-author, said: “On coasts like Derwent Howe, the process of lithification has turned a sandy beach into a rocky platform very, very quickly.
“That rapid appearance of rock could fundamentally affect the ecosystems above and below the water, as well as change the way that coastlines respond to the challenges of rising sea levels and more extreme weather as our planet warms.
“Currently, none of this is accounted for in our models of erosion of land management, which are key to helping us try to adapt to climate change.
“We’re currently seeking additional funding to help support further research at other slag deposit sites across Europe, which will help to deepen our analysis of this new rapid anthropoclastic rock cycle.”
The research is published in the journal Geology.
免责声明:info@kdj.com
所提供的信息并非交易建议。根据本文提供的信息进行的任何投资,kdj.com不承担任何责任。加密货币具有高波动性,强烈建议您深入研究后,谨慎投资!
如您认为本网站上使用的内容侵犯了您的版权,请立即联系我们(info@kdj.com),我们将及时删除。
-

-

- 价格预测palooza:突破,重新测试和一堆加密魔法
- 2025-08-03 05:58:08
- 导航加密货币景观?我们正在深入研究价格预测,突破策略以及支持重测的关键作用。准备狂野!
-

-

-

- Litecoin,USDC和2025年的采矿:纽约人的拍摄
- 2025-08-03 04:00:07
- 在2025年在Litecoin,USDC和采矿世界中浏览世界。发现云采矿,Stablecoin策略和最新趋势。
-

- 比特币,微观和机构信心:看涨的三杆?
- 2025-08-03 03:41:01
- MicroStrategy的持续比特币积累信号信号是强大的机构信心,可能会重塑加密市场。这是持续牛的开始吗?
-

- Ruvi AI令牌:预售里程碑后即将上涨?
- 2025-08-03 03:31:02
- Ruvi AI的预售成功,CMC上市和即将到来的价格上涨正在转向。这是加密货币中的AI驱动令牌吗?
-

- Ruvi AI:百万富翁制造商的价格飙升了吗?
- 2025-08-03 02:00:59
- Ruvi AI将引起嗡嗡声,成为下一个潜在的“百万富翁代币”。发现其AI驱动的超级应用程序和战略预售如何导致巨大的收益。
-

- DOGE,公用事业硬币和聪明的钱:加密投资的新时代?
- 2025-08-03 02:00:23
- Doge的模因魔术褪色吗?聪明的钱正在注视公用事力硬币。发现为什么专家在不断发展的加密景观中从炒作转移到实质。