|
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
分析海灘如何變化並可能在將來發生變化,這並非易事。為了做出準確的預測,研究人員需要有關複雜力量和因素的數據

The most constant thing about beaches is that they are always in flux. Wind, waves, and currents move sand around, building up shorelines in some places and eroding them elsewhere, with consequences for coastal wildlife, including birds. Analyzing how beaches change, and may change in the future, is no easy task. To make accurate predictions, researchers need data on a complicated array of forces and factors, from big-picture elements like topography and tides to the tiniest components of a coast: grains of sand.
關於海灘最持續的事情是,它們總是在不斷變化。風,波浪和電流在周圍移動沙子,在某些地方建立海岸線,並在其他地方侵蝕它們,並對包括鳥類在內的沿海野生動植物產生後果。分析海灘如何變化並可能在將來發生變化,這並非易事。為了做出準確的預測,研究人員需要有關複雜力量和因素的數據,從地形和潮汐等大型元素到海岸最小的組成部分:沙子的穀物。
But until recently, sand has been relatively understudied. Enter SandSnap—a collaborative project sponsored by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, James Madison University, and consultancy Marda Science LLC. Since 2022, the project has enlisted community scientists to build a database of beach sand across the United States, from both freshwater sites like the Great Lakes and ocean beaches. The information will support beach restoration projects, including habitat for at-risk shorebirds like Red Knots and terns
但是直到最近,沙子已經相對研究了。輸入Sandsnap - 由美國陸軍工程兵團,詹姆斯·麥迪遜大學和諮詢公司Marda Science LLC贊助的合作項目。自2022年以來,該項目已邀請社區科學家從大湖區和海洋海灘等淡水地點建造一個在美國各地的沙灘數據庫。該信息將支持海灘修復項目,包括紅色結和燕鷗等高危岸邊的棲息地
The SandSnap database currently contains some 2,800 analyzed images of beach sand, along with their latitude, longitude, and a measure of grain size—a crucial factor in how beaches change over time. The process is simple: Participants go to a debris-free section of dry sandy beach, place any coin on the sand for scale, snap a photo with a cell phone, and upload the image to the project's web site. Analysts measure the sand’s grain size using a deep-learning neural network trained on a range of sediment samples from diverse locations. Slightly more than 70 percent of the existing images are from U.S. beaches; the rest are from sites worldwide.
Sandsnap數據庫目前包含大約2800張經過分析的沙灘圖像,以及它們的緯度,經度和晶粒尺寸的度量,這是海灘隨時間變化的關鍵因素。該過程很簡單:參與者轉到干沙灘的無碎屑部分,將任何硬幣放在沙灘上以獲取比例尺,用手機拍攝照片,然後將圖像上傳到項目的網站上。分析師使用在不同位置的一系列沉積物樣本中訓練的深度學習神經網絡來測量沙子的晶粒尺寸。現有圖像中有70%以上來自美國海灘;其餘的來自全球的網站。
Sand comes in many sizes and shapes, reflecting the rocks and shells that produced it and the geologic processes that wore them down. “Beaches exist in a rough equilibrium between the size of the waves and the size of the sand-grains,” says David Young, an Army research engineer. The larger sand-grains are, the more energy it takes to move them, so the presence of finer sands and clays indicates that a beach has small, gentle waves. If bigger sand-grains start washing up, wave action is likely increasing. To build an accurate computer model of a shifting coastline, scientists need to know the exact size of the beach’s sand-grains. But no comprehensive database of sand-grain sizes in North America exists, and collecting this information would be prohibitively expensive for any single agency or laboratory, especially because the composition of beach sand changes over time. Since beaches are popular destinations, community scientists are well positioned to help fill the knowledge gaps.
沙子有多種尺寸和形狀,反映了產生它的岩石和貝殼以及使它們磨損的地質過程。陸軍研究工程師戴維·揚(David Young)說:“海灘在海浪的大小和沙粒的大小之間存在粗糙的平衡。”較大的沙粒是移動它們所需的能量,因此較細的沙子和粘土的存在表明海灘有小而柔和的海浪。如果較大的沙粒開始洗滌,波浪動作可能會增加。為了建立一個不斷變化的海岸線的準確計算機模型,科學家需要知道海灘沙粒的確切尺寸。但是,北美沒有全面的沙粒大小數據庫,並且對於任何單個機構或實驗室而言,收集此信息都會非常昂貴,尤其是因為海灘砂的組成隨著時間而變化。由於海灘是受歡迎的目的地,因此社區科學家在幫助填補知識空白方面處於良好狀態。
Though the Corps is best known for dredging rivers, harbors, and channels to keep ship traffic moving nationwide, the agency also restores or creates tens of thousands of acres of wetlands every year, sometimes using dredged sand to do so. “The Corps used to dump a lot of valuable dredged sediments offshore, but they’ve become better partner in reusing some of it,” says Brad Winn, vice president for resilient habitats at Manomet Conservation Sciences. Currently, the agency reuses about 30 to 35 percent of the material it dredges from waterways for so-called “beneficial purposes,” such as habitat restoration, and aims to increase that figure to 70 percent by 2030.
儘管該軍團以挖溝,港口和渠道以保持船舶交通的全國移動而聞名,但該機構每年還可以恢復或創造成千上萬英畝的濕地,有時使用疏gried的沙子來做到這一點。 Manomet保護科學彈性棲息地副總裁布拉德·溫恩(Brad Winn)說:“過去的軍團曾經在海上傾倒許多有價值的疏es礦石,但它們在重新利用其中的伙伴方面已經成為更好的合作夥伴。”目前,該機構重新以所謂的“有益目的”(例如棲息地恢復)重新挖出水道挖出的材料的30%至35%,並旨在到2030年將這一數字提高到70%。
But to meet that goal, federal engineers need more information about sand sizes and types at specific locations. Dredged material can’t be dumped randomly on the shore. “The sand needs to match the sand on the beach in size and color,” Young says. If the sand size and composition doesn’t match what’s already present, dredged material can wash away or change the profile of the beach—and that could harm shorebird species that rely on the habitat to nest or to feed during migration. Intertidal shoals, zones exposed at low tide and underwater at high tide, are “a grocery store for species like plovers, oystercatchers and migratory sandpipers,” Winn says. Foraging shorebirds pluck invertebrates from wet sands and small fish from tidal pools. On dry beaches, birds find insects and marine organisms trapped in seaweed at the wrack line.
但是為了實現這一目標,聯邦工程師需要有關特定位置的沙子尺寸和類型的更多信息。挖土的材料不能隨機倒在岸上。揚說:“沙子需要與海灘上的沙子相匹配。”如果沙子尺寸和成分與已經存在的材料不符,則挖土的材料可以洗淨或改變海灘的輪廓,並可能損害依靠棲息地築巢或在遷移過程中餵食的棲息地物種。溫恩說,潮間帶,在潮汐低潮和水下暴露的區域是“雜貨店的雜貨店,適用於諸如plovers,牡蠣捕撈者和候選人的雜貨店”。從濕沙和潮汐池中的小魚中覓食的鳥鳥無脊椎動物。在乾燥的海灘上,鳥類發現昆蟲和海洋生物被困在毛皮線上的海藻中。
In recent years the Corps has used dredged sand and mud to restore or create bird habitat in locations around the country, from Cape May County, New Jersey, to Hampton Roads, Virginia, and Savannah, Georgia. Environmentalists would like to see this work expand. “Sea level rise, erosion of dry sand beaches, and loss of intertidal areas are serious threats to beach-nesting and migratory birds,” Winn says.
近年來,該軍團使用疏遠的沙子和泥土來恢復或在全國各地的地點恢復或建立鳥類棲息地,從新澤西州開普梅縣到弗吉尼亞州的漢普頓路和喬治亞州的薩凡納。環保主義者希望看到這項工作擴大。溫恩說:“海平面上升,干沙灘的侵蝕以及潮間帶的損失是對海灘和候鳥的嚴重威脅。”
For anyone inspired to submit images, Brian McFall, an Army coastal engineer, offers some tips. Your photograph should capture an area slightly larger than a business card, with the coin in the corner. “Make sure you can see the sand-grains in your image, and that they aren’t blurry,” McFall says. SandSnap data has already been included in a few
對於受到提交圖像的任何人,陸軍沿海工程師Brian McFall提供了一些提示。您的照片應捕獲比名片略大的區域,而硬幣在角落。 McFall說:“確保您可以看到圖像中的沙粒,並且它們不會模糊。”少量數據已包含
免責聲明:info@kdj.com
所提供的資訊並非交易建議。 kDJ.com對任何基於本文提供的資訊進行的投資不承擔任何責任。加密貨幣波動性較大,建議您充分研究後謹慎投資!
如果您認為本網站使用的內容侵犯了您的版權,請立即聯絡我們(info@kdj.com),我們將及時刪除。
-

- 套利冒險:信用額,卡巴和追逐加密貨幣利潤
- 2025-08-03 20:01:53
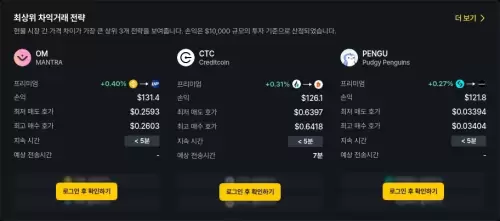
- 參與信用量(CTC)和Kaspa(KAS)套利的世界套利世界,探索實時市場效率低下的機會和風險。
-

- Solana的下一章:SOL預測和SOLF代幣嗡嗡聲
- 2025-08-03 18:01:14
- 探索Solana(Sol)達到新高度的潛力,這是由於Solf代幣周圍的嗡嗡聲及其對SPL社區的潛在影響。
-

-

-

-

-

-

- 索拉納的持久力:長期持有人和價格反彈
- 2025-08-03 17:35:02
- 隨著長期持有人加倍下降,探索索拉納的潛在反彈,這表明在市場波動中可能會恢復價格。 SOL是否捲土重來?
-

- 特朗普媒體的比特幣財政部:大膽的加密戰略還是冒險的賭注?
- 2025-08-03 17:33:14
- 特朗普媒體的$ 2B比特幣財政部引發了辯論。這是對財務彈性的明智之舉還是賭博?我們探索策略的風險和獎勵。